Extraction Of Caffeine From Tea Lab Report Conclusion

Caffeine was extracted from tea by the use of solid liquid and liquid liquid extractions.
Extraction of caffeine from tea lab report conclusion. The solvent methylene. Efficient extraction of caffeine from coffee relies heavily on the properties of caffeine other components present in coffee. Because caffeine is water soluble and is a base sodium carbonate must be added to the. The caffeine from the tea leaves was obtained by doing the extraction method.
A lab report 6 final copy. The percentage yield of caffeine is 89 98. The mass of this solid would reflect the actual yield of caffeine in the tea. However caffeine is not the only organic substance.
The solvents used in the experiment were an aqueous sodium carbonate and dichloromethane dcm. In this experiment caffeine was extracted from tea leaves then purified using sublimation. Using the proper extraction methods the caffeine within a tea bag could potentially be isolated to yield a pure solid. The amount of caffeine in a tea bag is 0 0979 g.
Elizabeth bellizio tyler hamby lisa nguyen. Objectives introduction results and discussion conclusion and. An organic solvent extraction was performed in this experiment. When you boil tea leaves tannins dissolve in the water as well as the caffeine.
Sodium carbonate and hot water were added to the tea bags and was let to stand for about 7 minutes in order to bring the caffeine molecules out of the tea bags and into the aqueous solution. Sodium carbonate was used because sodium carbonate acts as a base. Isolation of caffeine section 12 02 nattanit trakullapphan nam narissara pracharktam nik thaksaporn sirichanyaphong may abstract. This gave calculated values of 59 1 recovery and 40 9 error.
View lab report organic chemistry lab report distillation from chemistry 12 at national university extraction of caffeine from tea lab report of singapore. The caffeine was evaporated and appeared in yellowish form. To do so caffeine must be introduced to a solvent that is both volatile and insoluble to water. The base converts the.
If you do not use a base the tannins will also be extracted into the solvent used in the subsequent extraction. It is to be noted that its scale up can be done according to. The melting point of caffeine is 228 6. Anhydrous calcium chloride pellets were used to dry the solution and emulsion layer and the dcm was then decanted.
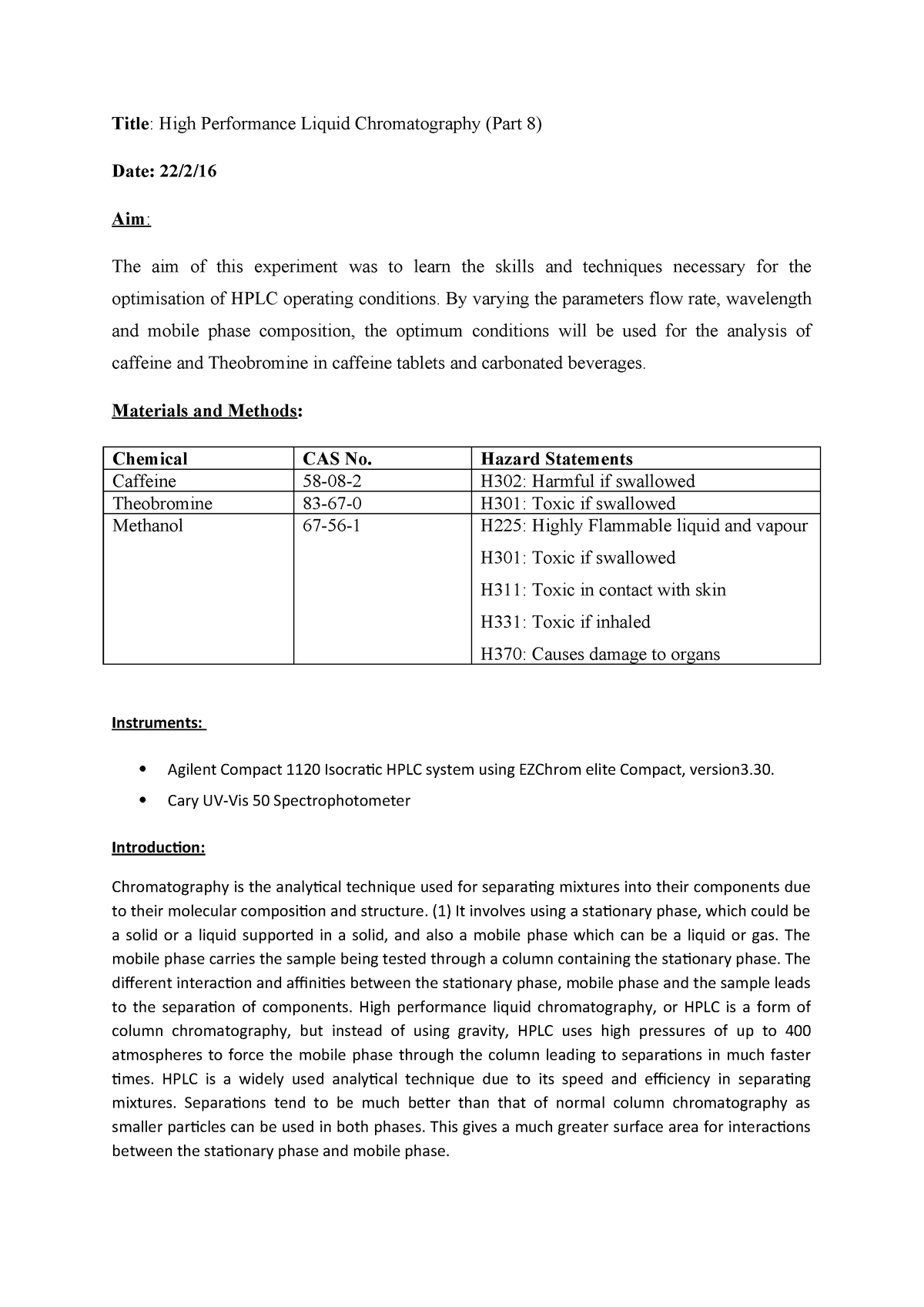
Lab report 5 final copy grade. Caffeine theobromine and theophylline in chocolate hplc uv. A pure product of 065 g caffeine was obtained. Conclusion in this experiment the caffeine was extracted from the tea bag.
Extraction of caffeine from tea. After washing the anhydrous calcium chloride pellets with more dcm the solvent was evaporated leaving. Product found in coffee and tea. Caffeine has a greater affinity for methylene chloride and will easily dissolve in this solvent over water.
The solution was then mixed with sodium carbonate. The purpose of this experiment was to perform a liquid liquid extraction method to extract the caffeine from the tea bags that were provided and then recrystallize the caffeine. An acid base liquid liquid extraction took place in order to force caffeine into the organic layer. By using separatory funnel the caffeine was separated from tea and coffee dissolved in.
In this experiment a solid liquid extraction method was used first to extract the caffeine room the tea leaves tea bags to by dissolving sodium carbonate in hot water and creating an aqueous sodium carbonate solvent. Caffeine can be extracted from tea by its ability to be better dissolved in dichloromethane than water. A perfect example is methylene chloride.